In the fast-paced world of electronics manufacturing, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) plays a pivotal role in delivering compact, efficient, and high-performance electronic devices. From smartphones to industrial control systems, SMT is the foundation upon which modern electronics are built. But what exactly is SMT, and why has it become the industry standard?
This blog breaks down the basics of SMT, its benefits, core processes, and widespread applications in today’s electronics industry.
What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
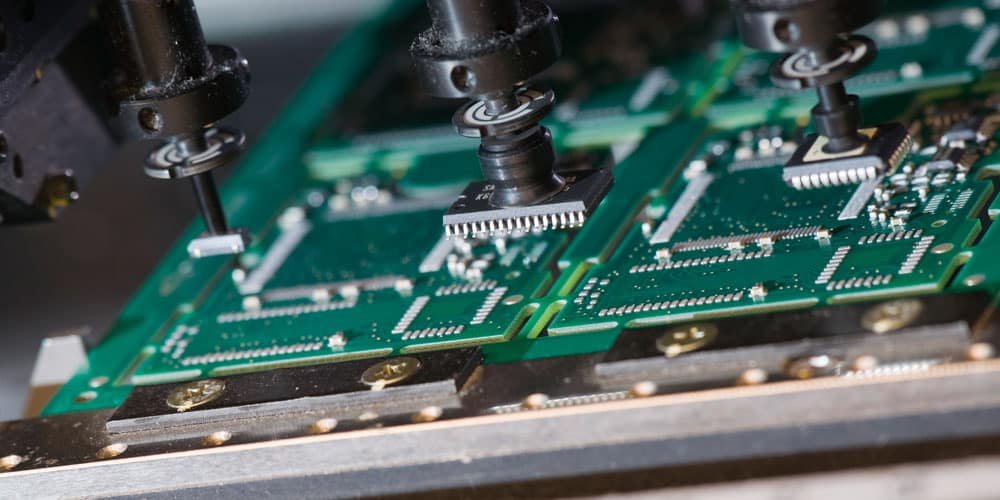
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method for producing electronic circuits in which the components are mounted directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These components are known as Surface-Mount Devices (SMDs). Unlike traditional through-hole technology, SMT does not require wires or leads to pass through the board, which allows for higher component density and smaller designs.
How Does SMT Work?
The SMT assembly process typically involves several automated stages:
- Solder Paste Application
A stainless steel stencil is used to apply solder paste to the pads on the PCB. - Pick and Place
High-speed pick-and-place machines accurately position SMDs onto the board. - Reflow Soldering
The board is passed through a reflow oven, where heat melts the solder paste to form solid electrical and mechanical connections. - Inspection and Testing
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection), X-ray, and functional testing ensure reliability and performance.
Advantages of Surface Mount Technology
SMT offers numerous advantages that have made it the preferred method in electronics manufacturing:
- Miniaturization
Enables the production of smaller, lighter devices with higher functionality. - Higher Component Density
Allows placement of components on both sides of the PCB. - Improved Performance
Reduced lead length results in better electrical performance and signal integrity. - Cost Efficiency
Automation reduces labor costs and increases production speed. - Reliability
Solder joints in SMT are generally more reliable due to better mechanical strength.
Applications of SMT in the Electronics Industry
SMT is used in nearly every sector of electronics manufacturing, including:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, TVs, wearables
- Automotive: ECU units, infotainment systems, safety modules
- Medical Devices: Diagnostic equipment, wearable monitors
- Industrial Control: PLCs, I/O modules, power controllers
- Telecommunications: Routers, signal boosters, base stations
Challenges in SMT Assembly
While SMT offers many benefits, it also comes with challenges such as:
- Thermal Management: Compact designs generate heat, which must be effectively dissipated.
- Component Handling: Smaller components are more prone to placement errors or damage.
- Inspection Complexity: Dense designs can be difficult to inspect without advanced equipment.
Conclusion
Surface Mount Technology has revolutionized how electronics are manufactured. Its ability to support compact, high-performance designs at high speed and low cost makes it indispensable in today’s digital world. Whether you’re an OEM, engineer, or hobbyist, understanding SMT is crucial to staying competitive in the electronics landscape.