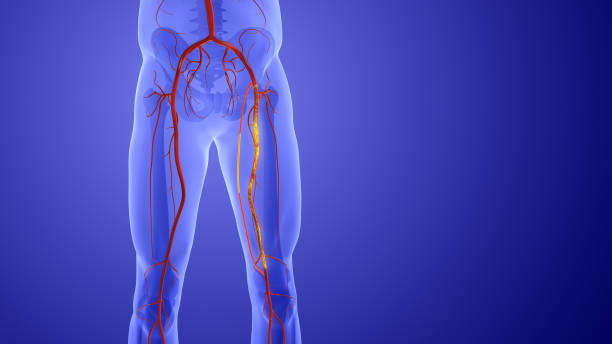
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD), also known as peripheral artery disease (PAD), is a common circulatory condition in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs. This condition can lead to pain, numbness, and an increased risk of infection. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Causes of Peripheral Vascular Disease
Peripheral vascular disease is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up in the artery walls. Several factors can increase the risk of developing PVD, including:
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for PVD, as it damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and contribute to atherosclerosis.
- High blood pressure: Hypertension can lead to artery damage and plaque buildup.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can increase the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to the development of PVD.
- Age: The risk of PVD increases with age, particularly after 50.
Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease
The symptoms of PVD can vary, but often include:
- Pain or cramping in the legs or hips during activities like walking or climbing stairs is known as claudication.
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Coldness in the lower leg or foot, especially compared to the other leg
- Sores or wounds on the toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly or not at all
- Change in color of the legs
- Diminished pulse or weak pulse in the legs or feet
Treatment Options
Treating peripheral vascular disease involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, medical procedures.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly can improve symptoms and overall vascular health.
- Medications
- Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms, lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and prevent blood clots.
- Supervised exercise programs
- Structured exercise programs can help improve symptoms and increase walking distance.
- Surgical Procedures
- In severe cases, procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow.
Seeking treatment in Singapore
Singapore offers advanced treatments for peripheral vascular disease, with experienced specialists providing personalized care plans.
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) is a circulatory disorder that narrows blood vessels outside the heart and brain, often affecting the legs. It occurs due to atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits (plaques) build up in arteries, restricting blood flow. Risk factors include smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and aging.
Symptoms:
Early signs include leg pain, cramping, or fatigue while walking (claudication), which eases with rest. Severe PVD may cause numbness, cold limbs, slow-healing wounds, or gangrene. Some people experience no symptoms, making regular check-ups crucial for high-risk individuals.
Diagnosis & Treatment:
Doctors diagnose PVD through physical exams, ankle-brachial index (ABI) tests, ultrasounds, or angiograms. Treatment focuses on improving circulation and preventing complications:
- Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, exercising, and eating a heart-healthy diet.
- Medications: Blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or blood pressure medications.
- Procedures: Angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery for severe blockages.
Early intervention can prevent complications like infections or amputations. If you have risk factors or symptoms, consult a healthcare provider promptly. Managing PVD improves mobility, reduces pain, and enhances overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Peripheral vascular disease can significantly impact quality of life if not managed properly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for maintaining vascular health and preventing complications. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can improve symptoms and enhance overall well-being.